The main objective of wastewater treatment is to allow domestic and industrial effluents disposal free of any danger to human health and ensuring the safety of the environment. Irrigation is the main method of utilizing effluent of wastewater. However, some wastewater treatment must take place before it can be used for agriculture or aquaculture.
A common question people ask is, what is the process of wastewater treatment? In this article, we provide you with answers to the question. If you want to learn more information, you can visit gustawater.com
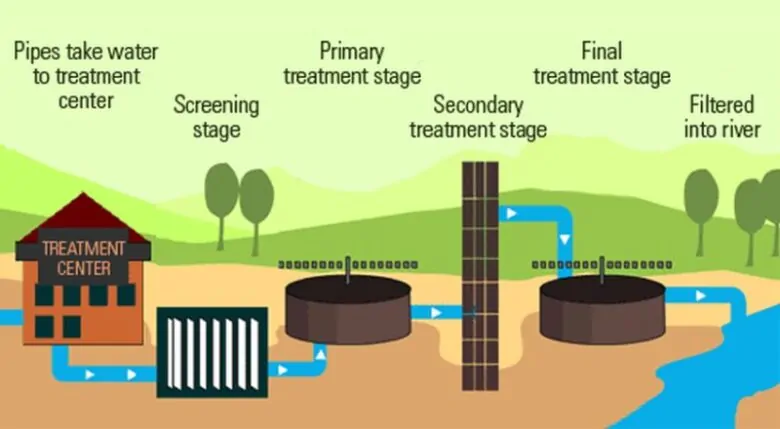
Conventional processes of wastewater treatment
It involves physical, biological and chemical processes. The procedures are used to remove organic solids matter, and nutrients from the wastewater. The following terms are used to describe different levels of treatment.
- Preliminary
- Primary
- Secondary
- Tertiary
- Advanced wastewater treatment
- Disinfection may be used to remove disease-causing organisms after the last process
Preliminary wastewater treatment
It is aimed at removing granular solids and large constituents found in wastewater. The materials are removed to improve the process and maintenance of treatment units. The preliminary process uses screening, gravel removal and comminuting of large matters. The velocity of water in the grit chamber is high and may use air to prevent settling of organic matters. The procedure is not normally used in small treatment plants. Sometimes comminutors are used as a supplement for coarse screening to decrease the size of large objects for removal as sludge. Devices used in the stage include flow measurement devices and standing-wave flumes.
Primary wastewater treatment
Its objective is to remove settled inorganic and organic matters after sedimentation. It is also used to remove the floating scum through skimming. It helps to remove biochemical oxygen demand (BOD), suspended solids (SS) and oil and grease. During primary sedimentation, some organic phosphorus, organic nitrogen, and heavy metals are also removed. The process does not affect dissolved and colloidal constituents.
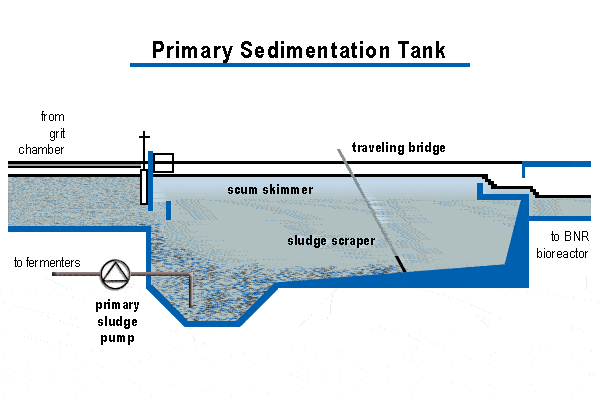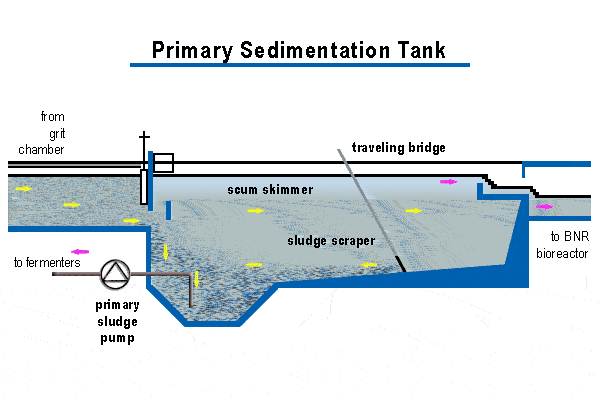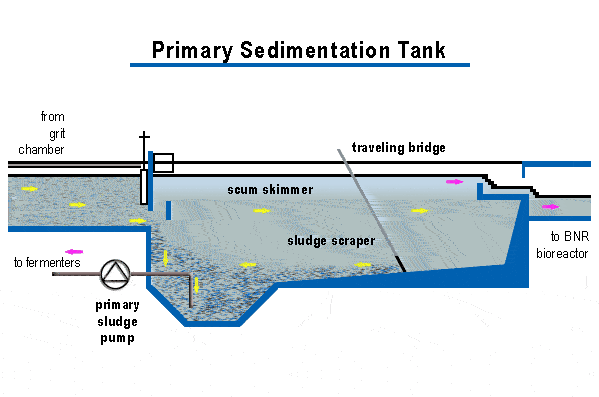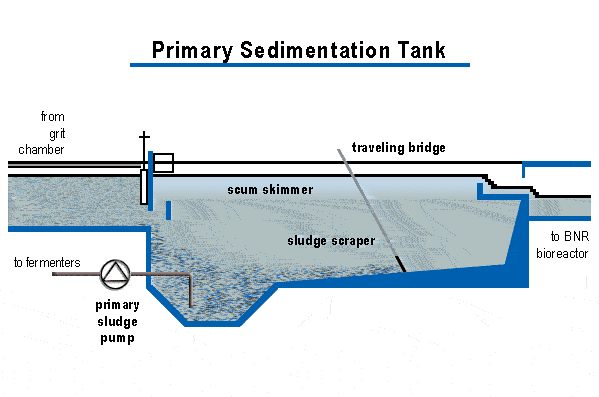
Primary sedimentation tanks are also known as clarifiers are 3 to 5 meters deep. Settled sludge is removed using sludge rakes into well for pumping. Scum is swept using water jets or mechanical means across the surface to sludge processing units.
Sludge is processed using biological means through anaerobic digestion. The process reduces the sludge volume, makes the sludge non-putrescible and improves the dewatering characteristics.
Secondary wastewater treatment
The objective of the process is to treat the effluent from primary treatment by removing the residual organics and suspended solids. It removes biodegradable and colloidal organic matter dissolved in the wastewater. The wastewater treatment process uses aerobic biological treatment by bacteria in the presence of oxygen. The products of this process are CO2, NH3, and H2O.
Microorganisms are separated from the treated wastewater to get the clarified secondary effluent. The process uses the following methods are a combination of more than one.
Activated sludge: it uses an aeration tank which contains wastewater and microorganisms. The contents are continually mixed by use aeration devices like fine bubble diffusers and supplied with oxygen. Agitation can also be done from the surface of the aeration tank.
Tickling filters: They are also known as biofilter and consist of a tower with support media. Microorganisms attach themselves on this media and wastewater is continually applied over the media. Oxygen is supplied naturally or through the use of blowers.
Rotating biological contactors (RBC): They are fixed film-film reactors like biofilters from which microorganisms attach themselves. They are rotating support media submerged in flowing wastewater reactor. Oxygen is transferred to wastewater through turbulence created by the rotation of the discs.
When combined with disinfection step provide substantial removal of virus and bacteria. The wastewater treatment process does not remove phosphorus, non-biodegradable organics, nitrogen, or minerals.

source:wikipedia.org
Tertiary wastewater treatment
The process is applied when specific wastewater impurities are not removed by the secondary process must be removed. There is an individual treatment for removal of phosphorus, nitrogen, additional suspended solids, heavy metals, refractory organics, and dissolved solids,
A modified activated sludge process is used to remove Nitrogen and phosphorus
Disinfection in wastewater treatment
It involves the injection of chlorine solution. The process is done in chlorine contact basins. The effect of chlorine on bacteria depends on PH, contact time, organic content and effluent temperatures.
Fine Bubble Diffusers
These are devices used in oxygen transfer during wastewater treatment. Oxygen is converted from gaseous state into a liquid during the process. Activated sludge requires more oxygen than supplied by surface air contact.
To achieve oxygen requirements in aerobic wastewater treatment plants, supply is done using additional interfaces like blowers and bubble diffusers.
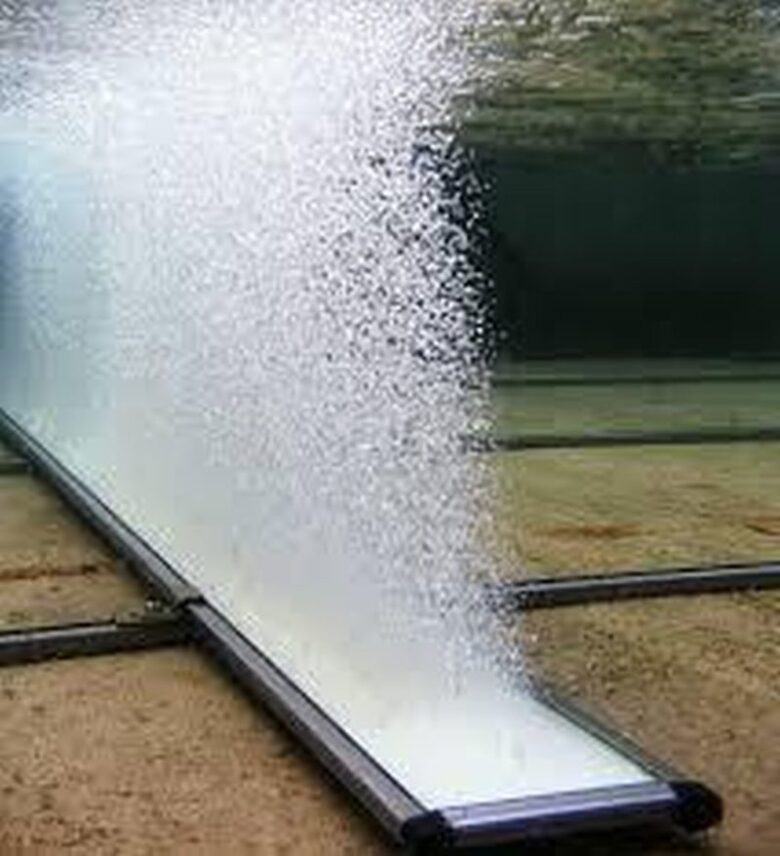

Fine bubble diffusers produce small air bubbles which rise from the floor of wastewater treatment plant aeration tank. The bubbles provide the quantities required of oxygen through mass transfer. Oxygen and food source allows bacteria to produce enzymes that breakdown the waste to allow settling in secondary clarifiers.
Fine bubble diffusers are made in different forms; tube, disc, dome, and plate.
Bubble size is important for aeration in wastewater treatment. Oxygen transfer efficiency helps in decreasing the power consumption. Fine bubble diffusers spread out evenly on the floor of the aeration tank.
Fine bubble diffusers advantages
- Diffusers prevent the tank contents from entering the supply lines. The membranes on fine bubble diffusers act as a valve thus preventing clogging.
- Fine bubble diffusers help in balancing air flow because the engineering is predictable and consistent.
- Small bubbles in large numbers transfer more oxygen due to increased bubble surface area. Fine bubble diffusers make it possible to achieve the desired amount of oxygen transfer using less air.
- Easy to adapt to existing tanks
- Lower emissions of volatile organic compound
- Best for high oxygen demand
Disadvantages of fine bubble diffusers
-
- Can be fouled by chemicals and biological activities.
- They are expensive.
- Air flow distribution is critical and requires the use of airflow control systems.
- Aeration tanks may have conflicting needs in terms of airflow and oxygen transfer.
Conclusion
Oxygen is required in wastewater treatment. Aeration process in activated sludge tanks requires the intervention of mechanical means to supply sufficient oxygen for microorganism to produce enzymes. Now you know what is the process of wastewater treatment, comment below if you need more information.

