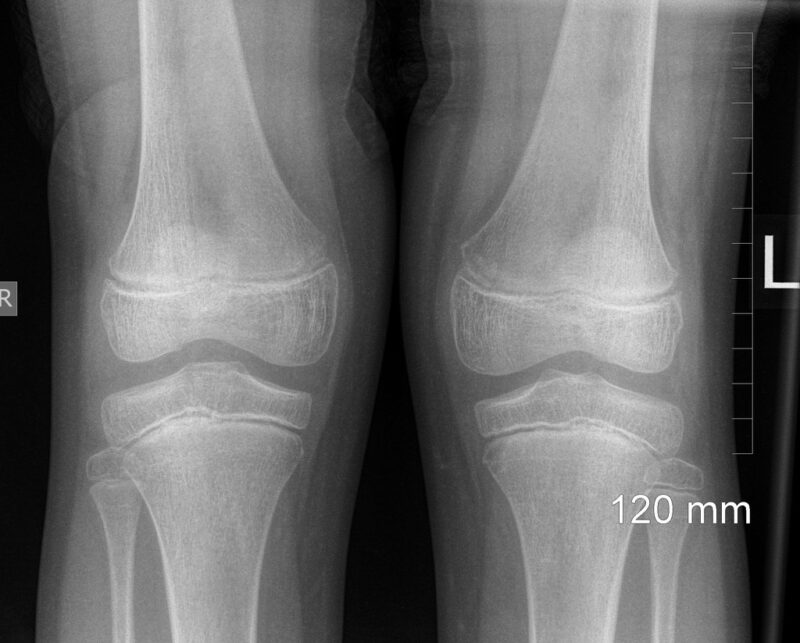
Knee pain, impaired joint mobility in this area, and traumatic injuries are quite common reasons for visiting a doctor. It is not easy even for an experienced doctor to determine by eye what the unpleasant symptoms are related to. But a diagnosis is not an essay on a free subject, and a surgeon, traumatologist, or orthopedist must rely on accurate information, which can be obtained by conducting additional diagnostic measures. One such mandatory and inexpensive examination is a knee X-ray.
Indications

An x-ray is a procedure that allows the doctor to see deep structures that are invisible to the human eye, which cannot illuminate the soft tissues to view denser formations. In contrast to a fluorogram, which must be taken regularly once a year, the doctor prescribes a knee X-ray only when there is a suspicion of certain pathologies affecting the bones, cartilage tissue, and ligament apparatus of the knee. This usually occurs when you go to the doctor for pain and limitation of leg movement, or when you are admitted to the emergency room for an injury.
What disorders and abnormalities may require X-ray confirmation?
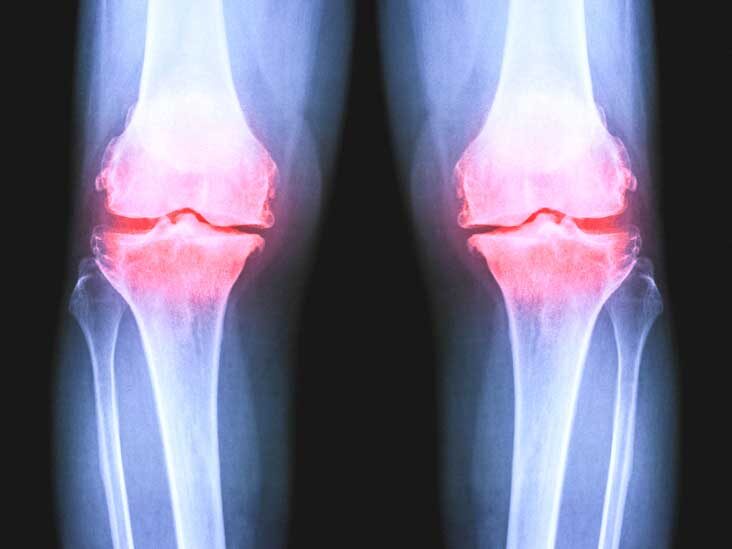
- Bone integrity disorders of the joint. The hard tissues – bones – are best viewed on X-rays, it is clear that such a study makes it possible to accurately diagnose any damage: fractures, the presence of cracks and dents formed as a result of a hard blow. The value of X-ray examination in this case also consists in the fact that the doctor receives information about the exact localization of the injury, the location of bone fragments, the size of cracks and bone indentations.
- Dislocation/subluxation of the joint. The bones are misaligned relative to each other to judge the nature of the dislocation. In a joint, the bulge of one bone should coincide with the depression in the other. Any misalignment can be evidence of bone displacement as a result of impact or careless movement.
- Ligamentous apparatus injuries (tears, sprains). Their presence is judged by the distance between the bones, because ligaments themselves do not reflect X-rays in full, so they are poorly visible.
- Traumatic injuries of the kneecap (patella) and meniscus (inner and outer cartilage). Also detected by displacement of the bone or the presence of cracks in it
- Congenital pathologies of bones and joints (osteodystrophies and osteopathies).
X-ray examination allows you to make an accurate diagnosis in case of:
- arthritis and arthrosis (changes in the shape of the joint and the size of the joint gap are observed),
- Osteoporosis and osteomyelitis (changes in bone density in different areas, unusual layers may appear)
- Synovitis (due to the accumulation of fluid in the deer and increased thickness of the synovial capsule, the joint gap increases)
- Kenig’s and Osgood-Schlatter’s osteochondropathies (foci of bone necrosis with smooth, jagged edges are detected).
- Radiography of the knee joint can also reveal pathologies that the patient did not even suspect. For example, tumor processes affecting the bones and soft tissues of the joint, the presence of cysts and unusual bone growths (osteophytes), and the presence of a foreign body.
Applying to the doctor with complaints of pain in the area and changes in the shape of the knee (regardless of whether the person has had an injury), impaired mobility of the knee joint, swelling and reddening of soft tissues, indicating an inflammatory process, are already good reasons for ordering an X-ray examination.
Preparation

A knee X-ray is considered to be a procedure that does not require any preparation. A person can go for the examination immediately after consulting a doctor. X-rays of different parts of the lower extremity do not require restrictions on diet and medications. And even in the case when it is carried out with contrast. The fact is that the contrast is not injected into a vein, but directly into the joint capsule. The only thing that may be necessary is an allergy test to detect the sensitivity of the body to contrast.
Before the procedure, it is advisable to expose the area under study, as clothing may contain details that distort the radiographic image. If the patient was previously bandaged on the knee area, there is no need to remove it, but the devices, which fix the leg after the injury in the right position, will have to be removed if possible.
Since the lower part of the body is exposed to radiation, a special lead apron is put on the area of the childbearing organs, which prevents the passage of X-rays. However, this is more relevant for children, whose body size is smaller than that of adults, which means that the X-rays can also capture a small part of the child’s body. For more information, visit mricfl.com.
Knee X-ray technique
X-rays of the knee joint of an infant (and it may be required in connection with birth traumas and congenital pathologies) are performed with the utmost caution. The whole body of the baby is covered with special protective devices. This is due not only to the fact that irradiation is more dangerous for the baby than for an adult. The infant’s height is still very small, so the whole body, not just the limb to be examined, may fall into the field created by the X-ray radiator.
There are no special nuances to X-rays. The main requirement is to be in the static position indicated by the doctor. Any movement will cause distortions in the images, making diagnosis difficult. Often in such cases, repeat radiographs are required, which is an additional dose of x-rays.
It is most difficult to hold a child in a stationary position, so the x-ray table is equipped with special fixation devices. If the cause of anxiety is pain, the patient may receive a shot of anesthetic for a high-quality examination.
For an accurate diagnosis of the pathologies described above, you usually need at least 2 X-rays in different projections. Straight projection (the picture is taken when the person lies on his or her back) is the most indicative when fractures of the bones in the joint are suspected. When standing, several images can be taken: lateral, tangential, and transcondylar projections. The latter, if necessary, can be taken lying on your side.
The tangential projection better reveals patella pathology and inflammatory and degenerative joint changes. The transcondylar projection is prescribed to detect ligament sprain, necrotic processes in bone tissue, and suspected osteoarthritis. But in the lateral projection you can diagnose fluid accumulation in the joints.
In some cases, doctors are limited to a single projection, but when the diagnosis is controversial, it is still more relevant to consider images taken from different angles. Most often, doctors prescribe an X-ray of the knee joint in two projections.
The function of the different structures of the knee joint can be assessed by taking pictures of the leg bent at different angles. X-rays can be taken both at rest and under load.
Contraindications to performing
A knee X-ray is a procedure that involves the process of exposing a patient’s limb to harmful ionizing radiation. However, if you cover your body with protective clothing, the effects after the procedure will be minimal.
It is believed that exposure to X-rays has a negative effect on human health. In this case we are not talking about the symptoms typical for the early period after receiving a dose of radiation: reddening of the skin (radiation burn), detachment of the epidermis, the appearance of erosions, increased fatigue, etc. But different sources keep on talking about late complications after the procedure, such as increased risk of cancer, mutational changes, reduced sexual functions, etc.
In fact, such consequences are possible if x-rays are taken daily for a long period of time without protective equipment. But according to feedback from doctors and patients, they have not come across anything of the kind (at least there is no clear correlation between the symptoms that appeared subsequently and diagnostic measures).
The radiation dose in modern X-ray units when examining a knee joint is approximately equal to the radiation dose we receive in a day and a half of our life in natural conditions. At the same time, it is dozens of times less than the radiation that surrounds us in airports and airplanes. Therefore, even repeated shots are not capable of causing much harm to the body, even taking into account the radiation received while watching TV programs, working on a computer, etc.
Nevertheless, there are still some contraindications to the procedure. It is undesirable for pregnant and nursing women, since radiation can have a negative impact on the development of the fetus in the womb and can penetrate into the breast milk, and with it, into the body of the newborn. If there is no other alternative, a woman’s entire body with the exception of the knee should be protected from X-rays.
X-rays negatively influence the quality of sperm, so for some time after the procedure it is necessary to abstain from sexual intercourse, the purpose of which is to conceive a child. But x-ray results of obese people may not be reliable due to the high density of adipose tissue, which makes the images blurred.
It is undesirable to prescribe X-rays to people diagnosed with schizophrenia, as well as to patients who are in a very serious condition with signs of blood loss.
If a child is being diagnosed, it is better to choose safer methods if possible. The most popular diagnostic methods are ultrasound, computer and magnetic resonance imaging. The safest of all is considered all the same MRI, which uses magnetic field energy instead of X-rays.
All of these methods may be prescribed in conjunction with or instead of X-rays. Choosing what is better: ultrasound, CT or MRI, it should be understood that the difference between the studies is not only in safety for the body.
If the patient is faced with the choice of doing an MRI or X-ray of the knee joint, it should be understood that with solid tissue pathologies the X-ray study is preferable, i.e. the usual X-ray of the joint or a CT scan, which is also based on the penetrating ability of X-rays. At the same time CT scan is considered more informative for injuries and neoplasms in the knee area.
But MRI can easily diagnose diseases related to soft tissue structures: muscles, cartilage, ligaments, i.e. tissues with high water content, which react to the magnetic field.
True, the cost of computer and magnetic resonance imaging is much higher than a simple X-ray, which is considered quite sufficient for diagnosing knee joint pathologies.
Choosing ultrasound or X-ray of the knee joint, you must remember that the latter, although less safe, is more informative for the diagnosis of bone pathologies. If we are talking about the ligamentous apparatus, synovial capsule and cartilage pathologies, it is better to prefer the ultrasound, the cost of which is still lower than the popular MRI.