Maintaining good oral hygiene is as important as maintaining good physical health. You can’t ignore your oral health as the results afterward will be scary. Visiting a dentist and taking a treatment done from them sounds scary to most of us.
Hence, one must prevent gum diseases as much as possible. However, there are times when people acquire some severe gum diseases. Afterward, they may require details about gum treatment planning and procedure. Let’s understand them in detail at Ideal Smiles Dental Care.
The Reasons Behind the Occurrence of Gum Disease
Bacteria’s are the main reason behind the occurrence of all gingival issues. They may cause redness, bleeding, swelling, and even damage to the bone present beneath the gingiva or the gums in your mouth. We may need immediate control of the spread of this bacterial infection.
As the consequences become severe, this situation afterward will cause uncontrollable damage to your teeth. The primary symptoms of this bacterial infection can be evident when the person starts experiencing sensitivity to hot and cold stuff. This may be a sign that they need gum treatment.
Symptoms of Severe Gum Diseases:
- Swollen and bleeding gums
- Bad breath
- Gingival recession
- Soft, red, and swollen gums
- Loose or mobile teeth
Gum disease treatment involves both surgical as well as non-surgical procedures. Both of them will be described and well explained in the ensuing article.
Non-surgical Treatment
-
Scaling
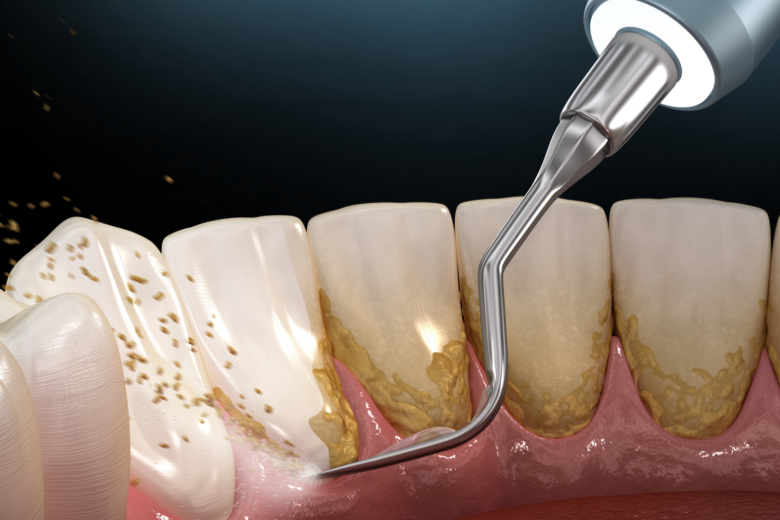
It is a non-surgical procedure for gum disease treatment. The patient receives an injection of a prescribed dose of local anesthesia. Afterward, the removal of tartar and plaque takes place. When the removal of bacteria below the gum line takes place, we call the procedure scaling.
Similarly, we call the procedure of smoothening to smoothen the rough spots on the root planning. By doing both these procedures, we remove the bacteria inside the mouth. We thus provide a clean surface to the gums.
-
Dental clean-up
We, at times, visit a dentist for a regular checkup. They may remove the tartar or plaque present around your gum line. They may also recommend professional cleaning of gums twice a year. This is more of a preventive gum disease treatment.
Surgical Treatment
-
Flap surgery
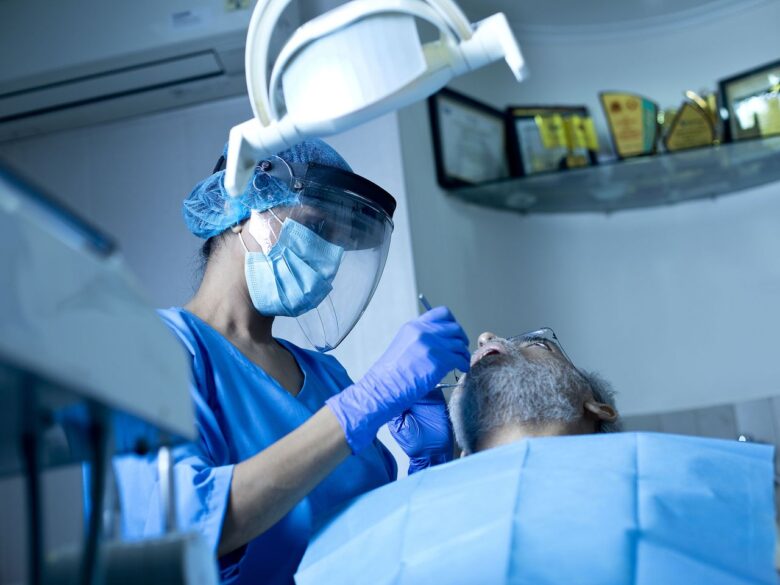
As the name suggests, the dentist raises a flap of the gums. They then remove the tartar present inside. They may also smoothen the uneven surface of the damaged bone. This limits the disease-causing bacteria. The dentist then places a raised flap of gums back in position. This process reduces the pockets between the gums and the tooth. As the dentist reduces these pockets, they, in turn, minimize the space for bacterial growth. This is a surgical gum disease treatment.
-
Soft tissue grafting
This procedure fills in the places of gingival recession. The dentist places a piece of a tissue graft from the top of the mouth. They then stitch it to the area of gingival recession. It grows and attaches there, thereby restoring the recessed gingiva.
-
Bone grafting
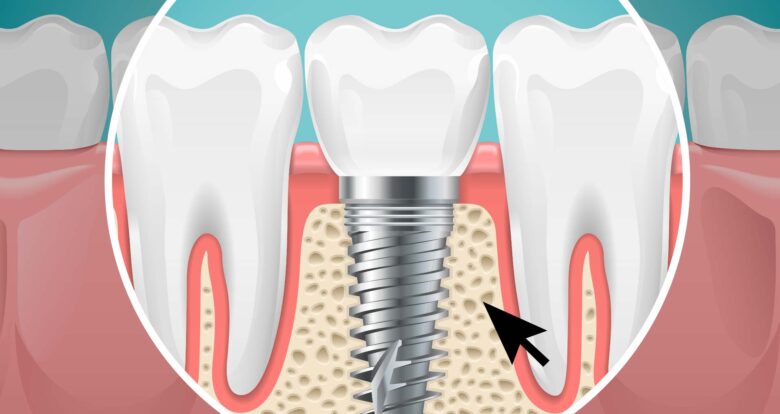
This process uses fragments from the person’s bone, donated bone, or synthetic bone. Afterward, the dentist does the replacement of the infected bone. Bacterial infection may destroy this infected bone by causing the spread of gingival infection. This bone graft serves to replace the lost bone. This, in turn, restores the stability of the teeth.
-
Tissue regeneration
A dentist performs tissue regeneration surgery when the destruction of the supporting tissues of the teeth occurs. As the name suggests, this procedure stimulates the growth of bone and the tissue of gums. This process may accompany flap surgery. While replacing the flap, the dentist places a piece of mesh between the gums and the bone. This method facilitates the growth of bone.
-
Bone surgery
Bone surgery prevents and resolves advanced bone loss. Surgical methods help to reduce the shallow craters over the bones. After the dentist performs flap surgery, the reshaping of alveolar bone takes place. This facilitates the filling up of all the cavities. If the craters cannot find space for growth, there will be fewer chances of periodontal infections. The development of the existing bacteria will also stop.
In most patients, the dentist performs gum disease treatment with the help of non-surgical methods. There are sporadic cases in which a dentist plans a surgical procedure.
Drugs for Treating Gum Diseases
A dentist may prescribe antibiotics in combination with surgical procedures or otherwise. Antibiotics may help to reduce bacterial growth and may also eliminate them. They may also help to slow down the destruction of tooth structures.
- Chlorhexidine helps to reduce the active microorganisms in your mouth. It controls the spread of plaque and periodontitis. The patient may use it as a mouthwash. Patients may also undergo placement of a chip in between the teeth and the gums.
- Dentists may also prescribe doxycycline, tetracycline, and minocycline to treat periodontal infections. These are antibiotics that will limit and prevent the spread of microorganisms. These microorganisms are responsible for causing these infections.
Apart from these drugs mentioned above, a doctor may prescribe specific kinds of toothpaste that may help to cure and resolve some of the periodontal tissues. Fluoride-rich toothpaste is the most essential medicine for this disease. Dentists may also prescribe toothpaste containing triclosan antibiotics. This keeps a check on plaque and tartar accumulation.
Conclusion

Maintaining good oral hygiene is very important. Even the slightest negligence on our end may invite bacterial growth and spread. Our oral cavity is made up of hard as well as soft tissues.
The bacteria attack the soft tissues such as the gums and multiply at these sites. There will be consequences if you do not take care of your mouth. You are not alone; the majority of people aged 35 and up are in a similar situation. Hence, one should be very careful while managing oral hygiene as well as bacterial spread.
Although, if you have already got an infection, the next thing you can do is to get a treatment done. There are surgical as well as non-surgical methods available for the same. A dentist may finalize the procedure based on the history and severity of the issue.


