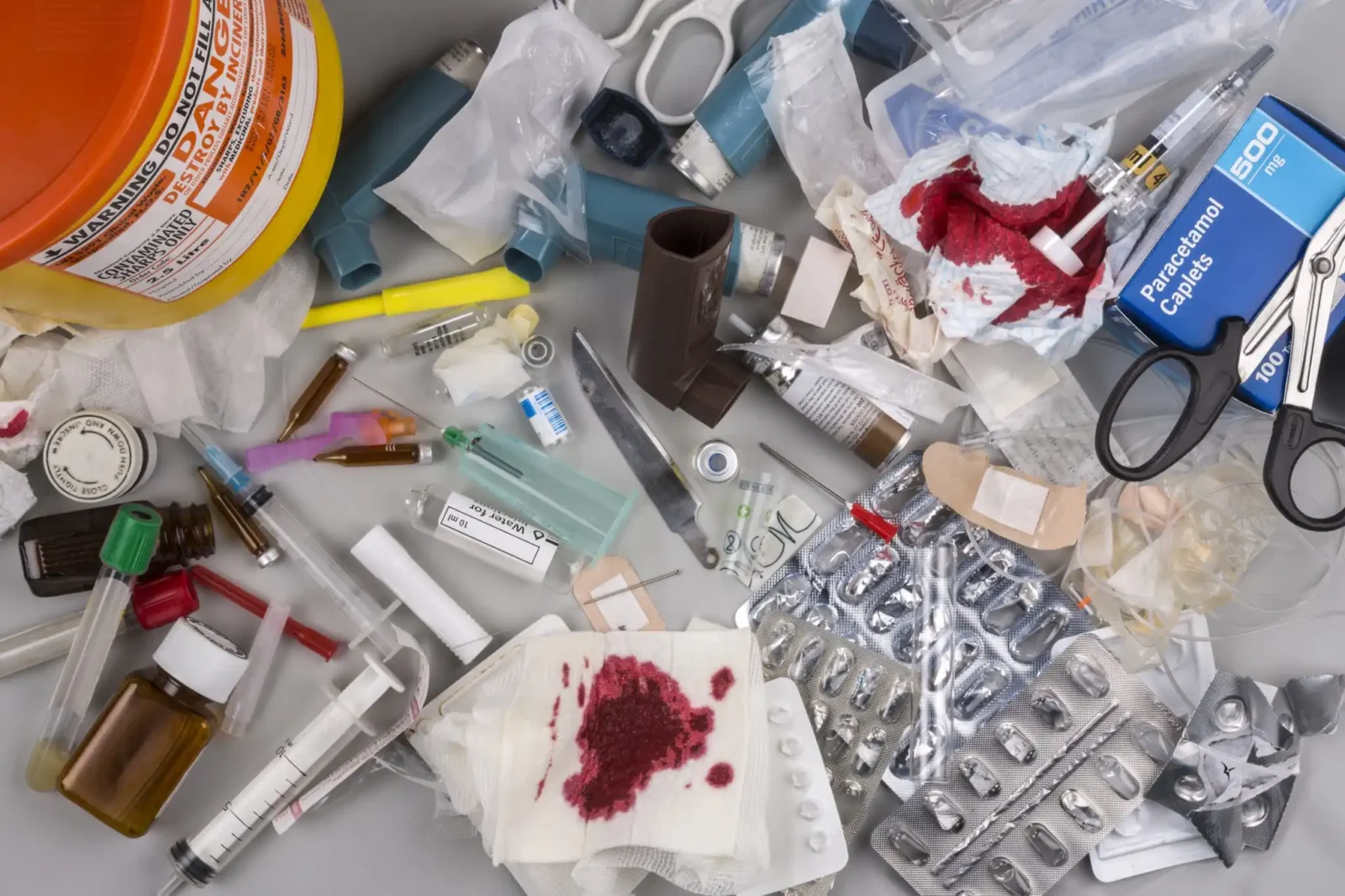
Medical waste is a residue of healthcare activities. As the healthcare industry grows with each passing year, so does medical waste production. It is estimated that out of the total healthcare waste, 15% falls under hazardous waste containing infectious and radioactive items. So, what waste items are considered medical waste, and what are the necessary protocols for healthcare waste management? In this blog, we will elaborately highlight medical waste types, waste handling guidelines, and more.
What is Medical Waste?
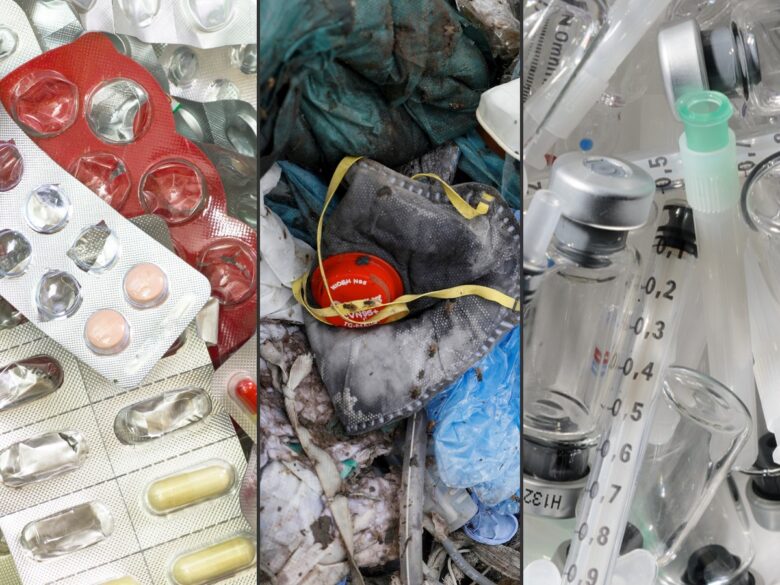

Medical waste is any waste that contains used or discarded medical items. These items include needles, syringes, gauze, body parts, blood, blood-contaminated items, chemicals, medical devices, pharmaceuticals, and radioactive items, among others.
Some common items that qualify as medical waste are:
- Blood-contaminated items, including gloves, gauze, syringes, and gowns
- Body parts of humans or animals, such as tissue, body fluid, organs, and blood
- Residues of cultures of infectious diseases
- Items used in chemotherapy, such as needles, PPE, drugs, and more
- Discarded drugs
- Any waste items that are in contact with a patient with infectious diseases
Medical waste is infectious or potentially infectious, posing the danger of spreading contamination if not disposed of carefully. Any leakage of this waste into our environment can expose us to disease-causing pathogens. Therefore, it is much more dangerous than household trash, requiring proper disposal methods to mitigate the risks of infectious contamination.
Here are some facts about medical waste:
- A single hospital produces around 33 pounds of medical waste each day.
- The U.S. generates over 5.9 million tons of medical waste each year.
- 85% of the total trash in medical facilities is non-hazardous.
- 2 million needles are produced as trash each day.
Different Types of Medical Waste
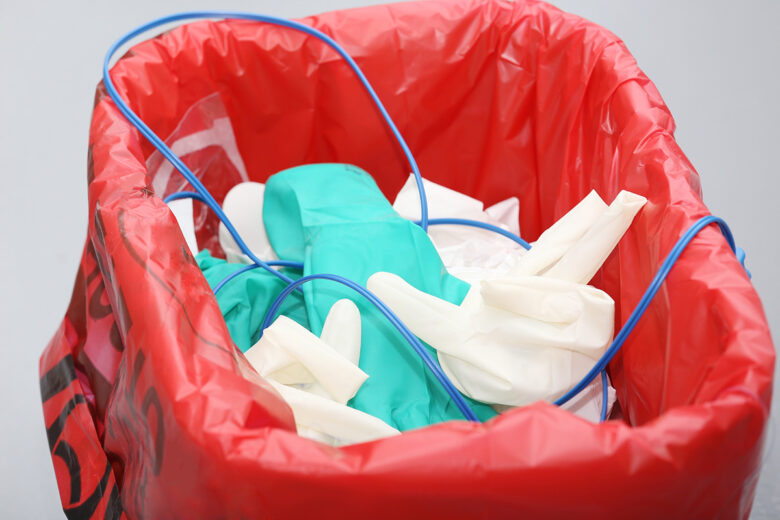

Medical waste can be broadly categorized into five major types, depending on the characteristics of the waste items. Each type of trash needs different methods of disposal for environmental safety. Here are the major classifications of waste produced by healthcare activities:
General Waste
A large amount of waste produced by medical facilities falls under general waste. These are non-contaminated items, including paper, plastic, and any other trash that is not hazardous or infectious. This type of waste does not pose the risk of serious health hazards.
Hazardous Waste
This type of waste contains toxic medical items that can cause various physical issues when exposed to them. It can cause breathing problems and irritation in the eyes and skin, among other physical ailments. Hazardous waste includes corrosive items, pesticides, herbicides, fluorescent bulbs, paints, chemical and pharmaceutical waste, poisons, batteries, and other items with mercury.
Radioactive Waste
Any waste that emits radioactive particles falls under radioactive waste. This type of trash can lead to severe ailments and dangerous environmental impacts. In healthcare, it is mainly produced as a result of radiation therapy. It includes waste items such as sharps exposed to radiation, clothing or tools used for radiation therapy, and any other disposable material that has come into contact with radiation.
Infectious Waste
The medical waste that is contaminated with infections falls under infectious waste. It includes items such as PPE, IV tubing, infected sharps, wound dressings, blood, body fluid, organs, and other pathological waste. Such waste can spread infectious diseases to people and contaminate the surroundings with deadly viruses and bacteria. It can contribute to the transmission of HIV, hepatitis B and C, parasitic infections, and so on.
Sharps
Sharps are sharp items that can potentially puncture our skin. It includes needles, scalpels, syringes, surgical knives, lancets, and autoinjectors. These are produced in large amounts in healthcare on a daily basis and require special care when handling. Sharps are collected and stored in specially designed, puncture-resistant bags for proper disposal.
Proper Practices for Handling Medical Waste
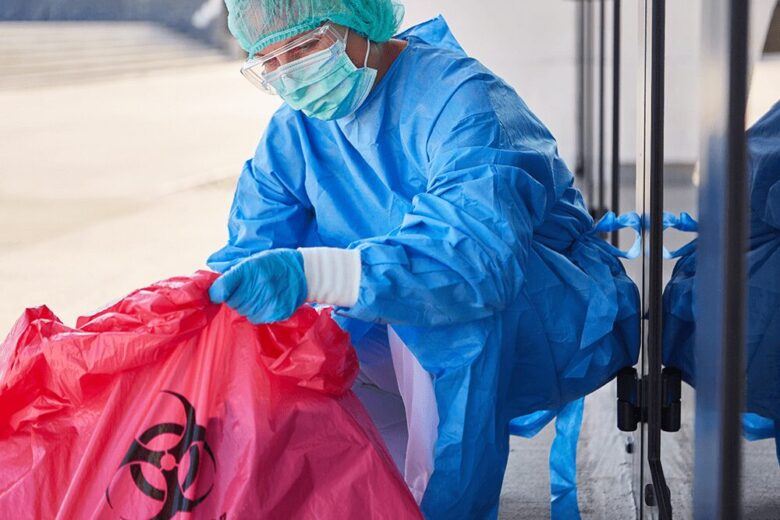

Negligence in handling medical waste can lead to severe long-term health issues such as HIV, hepatitis, infections, and more. Therefore, adhering to standard water handling practices will save you from potential dangers. Here are some tips on proper practices that you can follow to handle medical waste responsibly:
- Be aware of healthcare waste regulation laws and follow them strictly.
- Identify and classify the medical waste accurately.
- Separate the trash as per its type and collect it separately.
- Use the specified containers to store each type of waste.
- Adhere to the color code system of waste collection containers.
- Make sure to put on appropriate protective gear, including gloves, masks, and suits, while trash handling.
- Securely tighten the lids of the containers to prevent any leaks.
- Carry out proper chemical treatment for liquid and semi-liquid trash before disposal.
- Label the containers with the necessary details, including the types of trash in them.
Conclusion
It is essential to have a proper understanding of medical waste and handling processes, especially if you are a healthcare professional. The waste produced as a result of healthcare activities is highly toxic and infectious. It not only poses a threat to us but also severely degrades the quality of our environment. Therefore, to prevent potential hazards, medical waste is regulated and managed as per federal standards.
FAQs

Who generates medical waste?
Here are some common sources of medical waste:
- Hospitals
- Clinical laboratories
- Pharmacies
- Research laboratories
- Blood banks
- Dialysis and transfusion centers
- Mortuaries
- Veterinary clinics
- Nursing homes
- Dentist offices
What are the risks of medical waste?
Improper medical waste management can put us in danger of:
- Parasitic infections
- Lungs infection
- Meningitis
- Diseases from traces of vaccine
- Bacterial infection
- STIs
- HIV and hepatitis viruses
- Hemorrhagic fever
Who regulates biomedical waste?
The state environment and health agencies regulate your biomedical waste as per the regulations of your state. The federal authorities, such as the OSHA (Occupational Safety and Health Administration), FDA (U.S. Food and Drug Administration), and CDC (Center for Disease Control), among other regulatory agencies, are mainly involved in biomedical waste regulation.
Do I have to bleach my liquid biohazard waste before disposing of it?
Yes. You should always treat and sterilize the liquid biohazard waste before final disposal. Biohazardous waste contains contamination from infected blood and body fluids. The contaminants can easily spread in the surroundings if not disinfected properly before the final disposal. Bleach is a commonly used cleaning solvent for disinfection purposes. However, we can also use other chemical agents, including chlorine and sodium hydroxide.
What is the importance of labeling medical waste containers?
Labeling the waste containers will help you identify the type and degree of danger of waste stored inside the container. It allows you to safely handle the trash and protect yourself from the potential risks of exposure to hazardous materials. Besides, properly labeling the medical waste containers makes you compliant with waste regulatory standards.
Which color container indicates anatomical waste?
The anatomical waste is always kept in a red-colored bin. The red container is used to collect both animal and human body parts, such as tissue, organs, blood, and body fluids generated from surgical procedures, autopsies, or medical research. These anatomical wastes accumulated in the red container are highly infectious and need careful handling.