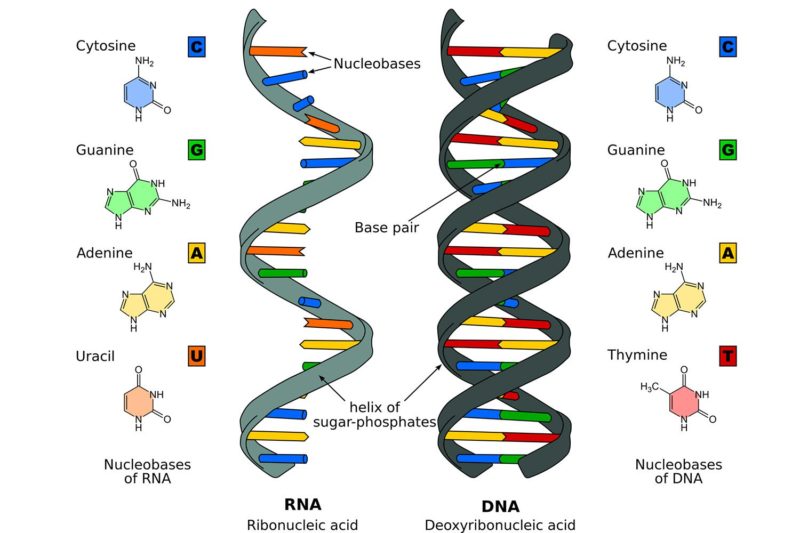
Vitamin B4, also known as adenine, is one of the five nitrogenous bases (cytosine, guanine, adenine, thymine and uracil) that helps make up the code in DNA and RNA. Adenine is a purine. Purines are six-membered rings attached to five membered rings. When Adenine is attached to DNA, it forms a bond with another molecule called Thymine, a pyrimidine, on the other side of the DNA strand. signal transduction as cyclic adenosine monophosphate, cAMP. Vitamin B4 (adenine) is a substance that acts as a co-enzyme with other substances, such as other vitamins to produce energy. Most of our energy comes from the mitochondria, which is the power producers of a cell. The mitochondria are like a power plant which burns fuel to produce the electricity that runs machinery.
Img Source: wikipedia.org
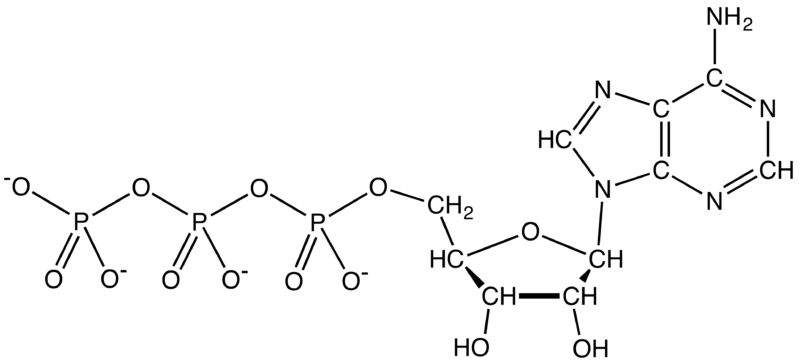
Besides DNA and RNA, adenine is also an important part of adenosine triphosphate, or ATP. Adenine forms adenosine, a nucleoside, when attached to ribose, and deoxyadenosine when attached to deoxyribose, and it forms adenosine triphosphate (ATP), a nucleotide, when three phosphate groups are added to adenosine. Adenosine triphosphate is used in cellular metabolism as one of the basic methods of transferring chemical energy between reactions. Adenosine triphosphate is the nitrogenous base adenine bonded to a five carbon sugar. This molecule is important because it has the ability to phosphorylize, or add a phosphate group to, other molecules. This transfer of a phosphate group allows energy to be released. It is this energy which is used by cells in living organisms. This is why the molecules ATP, and its nitrogenous base Adenine, are so important. Adenine is one of the two purine bases used in forming nucleotides of the nucleic acids DNA and RNA. In DNA, adenine (A) binds to thymine (T) to assist in stabilizing the nucleic acid structures. In RNA, adenine binds to uracil (U).
Img Sources: thoughtco.com
Adenosine plays an important role in biochemical processes. When administered intravenously, adenosine causes transient heart block in the AV node of the heart. In individuals suspected of suffering from a supraventricular tachycardia (SVT), adenosine is used to help identify the rhythm. Certain SVTs can be successfully terminated with adenosine. This includes any re-entrant arrhythmias that require the AV node for the re-entry (ie: AV reentrant tachycardia (AVRT), AV nodal reentrant tachycardia (AVNRT)). In addition, atrial tachycardia can sometimes be terminated with adenosine. Fast rhythms of the heart that are confined to the atria (i.e. atrial fibrillation, atrial flutter) or ventricles (ie: monomorphic ventricular tachycardia) and do not involve the AV node as part of the re-entrant circuit are not typically effected by adenosine. Because of the effects of adenosine on AV node-dependent SVTs, adenosine is considered a class V antiarrhythmic agent.The pharmacological effects of adenosine are blunted in individuals who are taking methylxanthines (ie: caffeine (even coffee) and theophylline).

Img Source: livescience.com
Adenine forms adenosine, a nucleoside, when attached to ribose, and deoxyadenosine when attached to deoxyribose, and it forms adenosine triphosphate (ATP), a nucleotide, when three phosphate groups are added to adenosine. Adenosine triphosphate is used in cellular metabolism as one of the basic methods of transferring chemical energy between reactions. These adenine derivatives perform important functions in cellular metabolism. Adenine is one of four nitrogenous bases utilized in the synthesis of nucleic acids. A modified form of adenosine monophosphate is thought to be a secondary messenger in the propagation of many hormonal stimuli. Adenine is an integral part of the structure of many coenzymes. Adenine is found in brewer’s yeast, whole grains (breads and cereals), raw unadulterated honey, bee pollen, royal jelly, propolis, most fresh vegetables, most fresh fruits.

